The energy landscape is evolving rapidly, with a growing emphasis on sustainability, efficiency, and reliability. Two key innovations at the heart of this transformation are smart grids and smart meters. In this article, we will explore how smart grids and smart meters are revolutionizing the gas and electricity sectors by enhancing efficiency, improving management, and enabling a more sustainable energy future.
Understanding Smart Grids and Smart Meters
- Smart Grids:
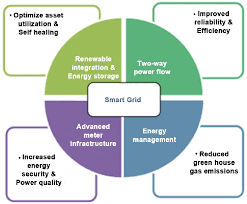
Smart grids are modern electricity grids equipped with advanced digital technology. They integrate communication, automation, and control systems into the electricity infrastructure, allowing for real-time monitoring and management. Smart grids improve the reliability, flexibility, and efficiency of electricity distribution.
- Smart Meters:
Smart meters are advanced measuring devices that replace traditional gas and electricity meters. They provide two-way communication between consumers and utility companies, allowing for remote data collection and enhanced energy management. Smart meters offer consumers real-time information about their energy usage and costs, enabling more informed decisions.
Benefits of Smart Grids and Smart Meters
- Real-Time Monitoring:
Smart grids and smart meters provide real-time data on electricity and gas usage, enabling consumers to make informed decisions about their energy consumption. This transparency encourages energy efficiency.
- Peak Load Management:
Smart grids can automatically adjust energy distribution during peak demand periods, reducing the risk of blackouts and the need for costly infrastructure upgrades.
- Renewable Energy Integration:
Smart grids facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, by managing intermittent energy production and ensuring a stable supply.
- Reduced Energy Waste:
Smart meters help identify energy waste and encourage consumers to adopt energy-efficient practices, ultimately reducing energy bills and carbon emissions.
- Enhanced Reliability:
Smart grids can identify faults and outages more quickly, leading to faster responses and improved service reliability.
- Demand Response Programs:
Smart grids and meters enable demand response programs, where consumers can voluntarily reduce their energy consumption during peak periods in exchange for incentives, helping to balance supply and demand.
- Carbon Footprint Reduction:
By promoting energy efficiency and the integration of renewable energy sources, smart grids and meters contribute to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions.
Challenges and Considerations
- Data Privacy and Security:
The collection of detailed energy data raises concerns about consumer privacy and data security. Robust data protection measures are essential.
- Infrastructure Investment:
Implementing smart grids and meters requires significant upfront investments in technology and infrastructure. Policymakers and utility companies must carefully consider the costs and benefits.
- Consumer Education:
Widespread adoption of smart meters and engagement with smart grids may require consumer education to ensure they can make the most of these technologies.
- Interoperability:
Ensuring that different smart meters and grid technologies are interoperable and can communicate seamlessly is crucial for their success.
Conclusion
Smart grids and smart meters are at the forefront of transforming the gas and electricity sectors, making them more efficient, reliable, and sustainable. These technologies empower consumers with real-time information about their energy usage, incentivizing energy conservation and reducing costs. Moreover, they play a pivotal role in integrating renewable energy sources, enhancing energy security, and reducing the environmental impact of energy production. As these innovations continue to evolve and expand, they will be instrumental in shaping a more efficient and eco-friendly energy future.